In our earlier article, we have explained 11 ways to find user account info and login details in Linux. One of the various commands we mentioned was the who command which displays users who are currently logged on to a Linux system, including the terminals they are connecting from.
This article will explain some useful examples of who command for Linux newbies.
The basic syntax for using who command is as follows.
$ who who [OPTION]... [ FILE | ARG1 ARG2 ]
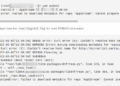
1. If you run who command without any arguments, it will display account information (user login name, user’s terminal, time of login as well as the host the user is logged in from) on your system similar to the one shown in the following output.
$ who ravi tty1 2018-03-16 19:27 tecmint pts/0 2018-03-16 19:26 (192.168.56.1) root pts/1 2018-03-16 19:27 (192.168.56.1)
2. To print the heading of the columns displayed, use the -H flag as shown.
$ who -H NAME LINE TIME COMMENT ravi tty1 2018-03-16 19:27 tecmint pts/0 2018-03-16 19:26 (192.168.56.1) root pts/1 2018-03-16 19:27 (192.168.56.1)
3. To print the login names and total number of logged on users, use the -q flag.
$ who -q ravi tecmint root # users=3
4. In case you want to show only hostname and user associated with stdin, use the -m switch.
$ who -m tecmint pts/0 2018-03-16 19:26 (192.168.56.1)
5. Next, to add user’s message status as +, - or ?, use the -T option.
$ who -T ravi + tty1 2018-03-16 19:27 tecmint + pts/0 2018-03-16 19:26 (192.168.56.1) root + pts/1 2018-03-16 19:27 (192.168.56.1)
The who command also helps you to view some useful system information such as last boot time, current runlevel (target under systemd), print dead processes as well as processes spawned by init.
6. To view the time of last system boot, use the -b flag and adding the -u option allows for listing of logged on users in the same output.
$ who -b system boot 2018-01-19 02:39
$ who -bu
system boot 2018-03-16 19:25
ravi tty1 2018-03-16 19:27 00:33 2366
tecmint pts/0 2018-03-16 19:26 . 2332 (192.168.56.1)
root pts/1 2018-03-16 19:27 00:32 2423 (192.168.56.1)
7. You can check the current runlevel with the -r option.
$ who -r run-level 3 2018-03-16 02:39
8. The following command will print dead processes.
$ who -d pts/1 2018-03-16 11:10 9986 id=ts/1 term=0 exit=0
9. Furthermore, to see active processes spawned by init, use the -p option.
$ who -p
10. Last but not least, the -a flag allows for printing of default output combined with information from some of the options we have covered.
$ who -a
system boot 2018-06-16 02:39
run-level 3 2018-01-19 02:39
LOGIN tty1 2018-01-19 02:39 3258 id=1
LOGIN ttyS0 2018-01-19 02:39 3259 id=S0
tecmnt + pts/0 2018-03-16 05:33 . 20678 (208.snat-111-91-115.hns.net.in)
pts/1 2018-03-14 11:10 9986 id=ts/1 term=0 exit=0
You can find more options by consulting the who man page.
$ man who
In this article, we have explained 10 who command examples for Linux newbies. Use the comment section below to ask any questions or give us your feedback.
Source: tecmint.com