Introduction
Jenkins is a unique automation server-based app that runs in a Java servlet container. The service supports a variety of Social Control Management (SCM) software systems such as SVN, Git, and Mercurial. It’s also a free software under MIT License.
This guide will take you through the process of installing Jenkins on an Ubuntu 18.04 VPS.. We will start by running Jenkins on our domain name hosting, then install it under Apache server and configure it as a reverse server proxy.
Before You Start
Before you begin, you need the following: An Updated Ubuntu 18.04 VPS or dedicated server.
Step 1 – Installing Java
Since Jenkins runs on Java, you need to start by installing Java OpenJDK on your server. Java can be installed from a PPA repository with the command below:
$ sudo apt install software-properties-common apt-transport-https -y $ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:openjdk-r/ppa -y
Next, install Java with the apt command:
$ sudo apt install openjdk-8-jdk -y
Once the installation process is done, confirm that the right java version has been installed successfully:
$ sudo java -version
Now, Java OpenJDK will be installed successfully on your Ubuntu server.
It is important to note that if your system has several java versions, use the following command to modify the java’s default version:
$ sudo update-alternatives --config java
Step 2 – Installing Jenkins
Jenkins features a functional repository for Ubuntu that is an essential package when installing Jenkins.
To add GPG keys and Jenkins repository to your system run the following command:
$ wget -q -O - https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable/jenkins.io.key | sudo apt-key add -
Once you have enabled Jenkins repository, run the command below to append the package repository for Debian to refer to the sources.list of your server:
$ sudo sh -c 'echo deb http://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable binary/ > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/jenkins.list'
Next, make the apt packages are up-to-date then install the most recent Jenkins version using the following command:
$ sudo apt update $ sudo apt install jenkins
Now, Jenkins will start automatically once the process is complete. Make sure you set it to start at boot time.
$ sudo systemctl start jenkins $ sudo systemctl enable jenkins
Check to confirm that Jenkins is working properly on Ubuntu 18.04:
$ sudo systemctl status jenkins
The following output will be displayed on your screen:
●jenkins.service- LSB: StartJenkinsatboottime Loaded: loaded(/etc/init.d/jenkins;generated) Active: active(exited)sinceWed2018-09-2215:18:22PDT;5min32sago Docs: man:systemd-sysv-generator(8) Tasks: 0(limit:2319) CGroup: /system.slice/jenkins.service
Step 3 – Configuring UFW Firewall
Jenkins is designed to run on port 8080. In this step, we’ll open this port via the ufw:
$ sudo ufw allow 8080
Next run the command below to confirm the ufw status:
$ sudo ufw status
This will give you an output similar to:
Status: active To Action From -- ------ ---- OpenSSH ALLOW Anywhere 8080 ALLOW Anywhere OpenSSH (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6) 8080 (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)
In case, the ufw is inactive, execute the commands below to activate it and enable OpenSSH
$ sudo ufw allow OpenSSH $ sudo ufw enable
That is it! The firewall is fully configured, plus Jenkins is installed. That means, you can now proceed with the initial Jenkins setup.
Step 4 – Configuring Jenkins
To Configure Jenkins after it’s installed, go to port 8080 on your browser, enter your domain name and IP address then http://your_ip_or_domain:8080. The following screen will appear:
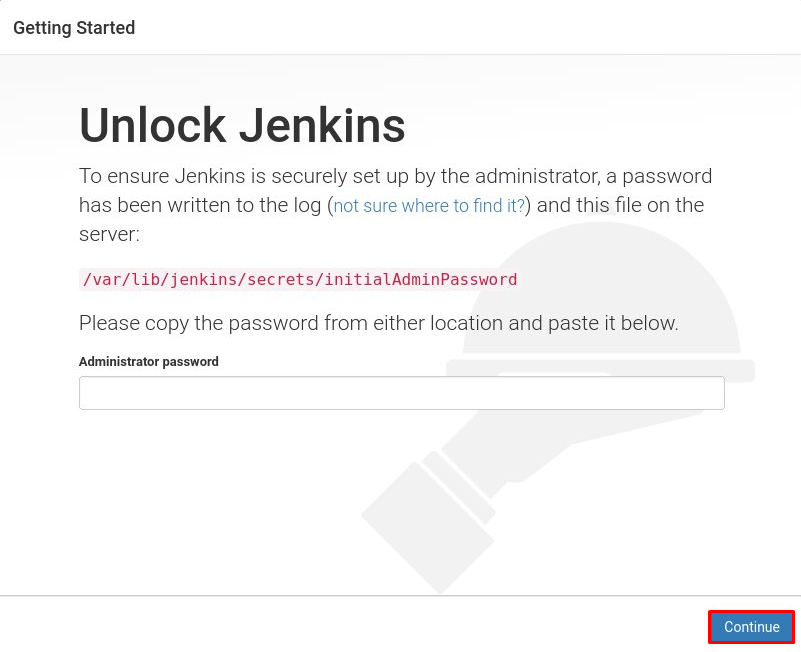
In the installation process, Jenkins installer automatically creates a password with 32 characters. To copy the password file to your terminal using the command below:
$ sudo cat /var/lib/jenkins/secrets/initialAdminPassword
Locate the Administrator Password box and enter the password then press Continue.
You will get a screen that prompts you to install some recommended plugins for Jenkins. Select Install Suggested Plugins.
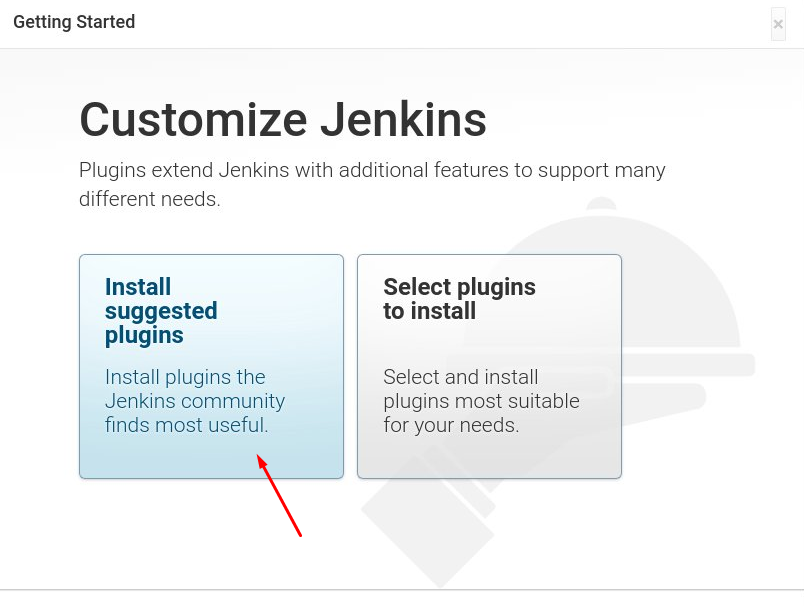
The next page will show that the installation is in progress.
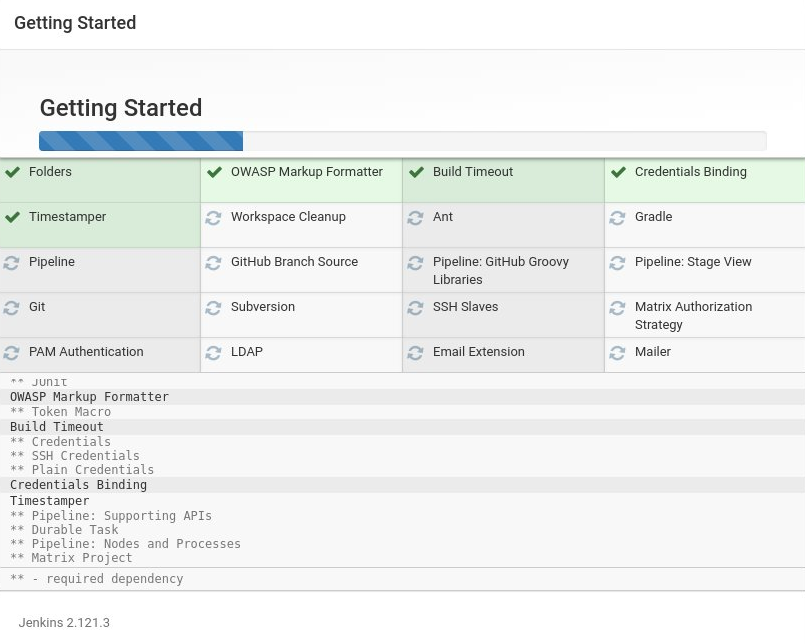
After Jenkins plugins are implemented successfully, you will be asked to create an admin account. Enter the required information then press Save and Continue.
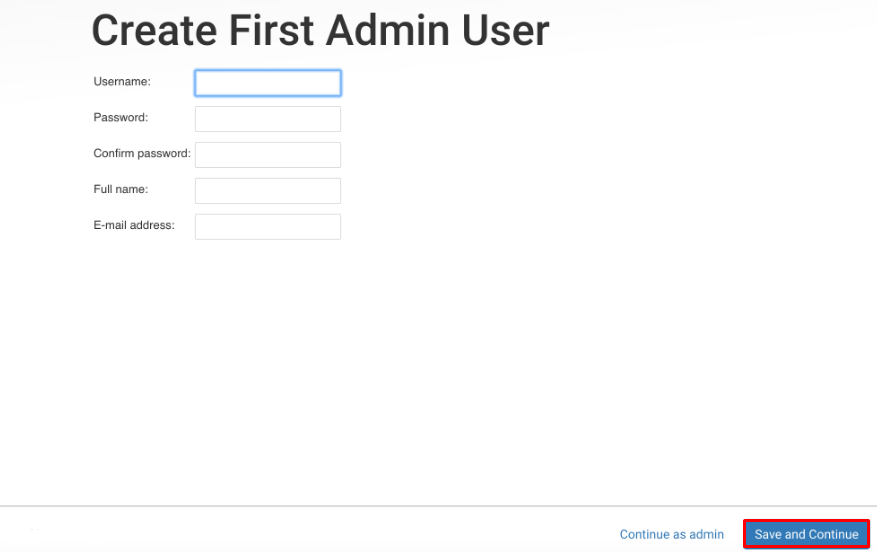
You will be prompted to enter Jenkins instance URL. Include the domain for Jenkins then press Save and Finish.
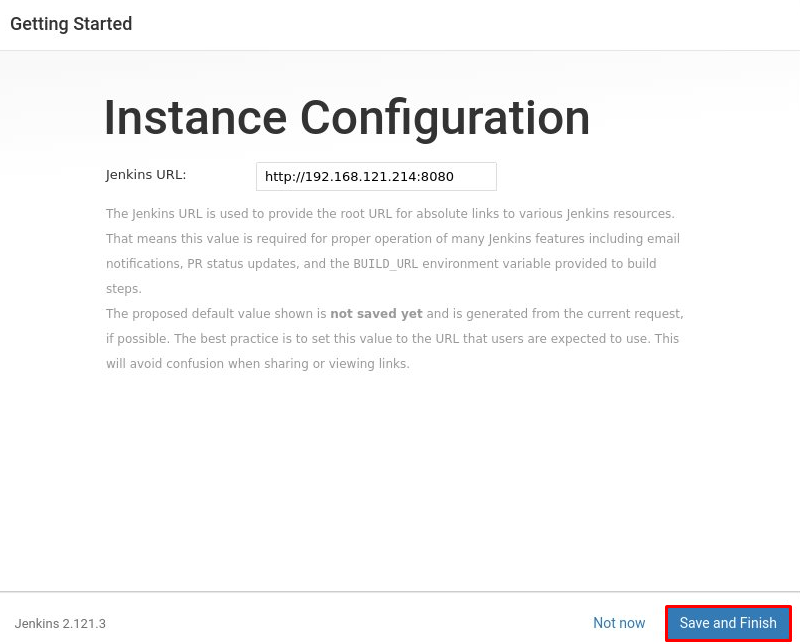
After the admin user account is created, you will get a confirmation screen showing “Jenkins is ready.”
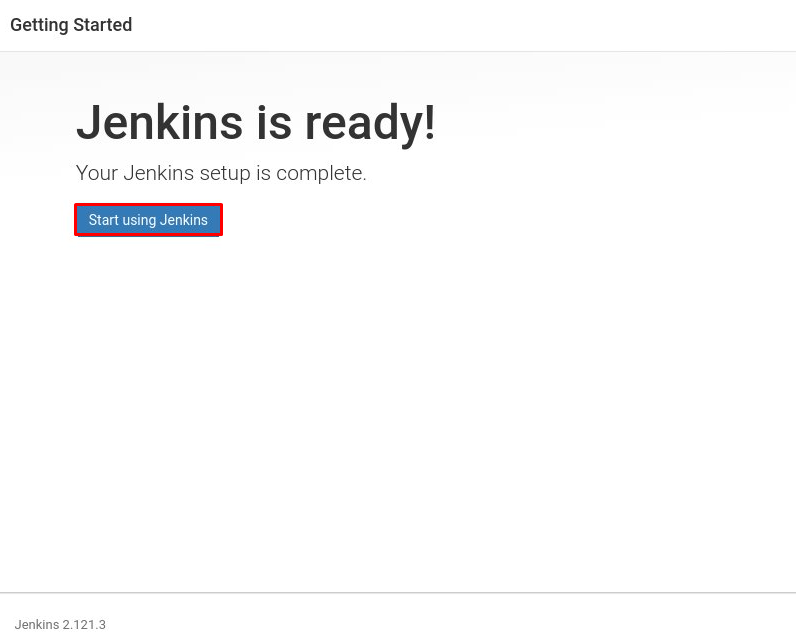
To visit Jenkin’s main dashboard page, press “Start using Jenkins.”
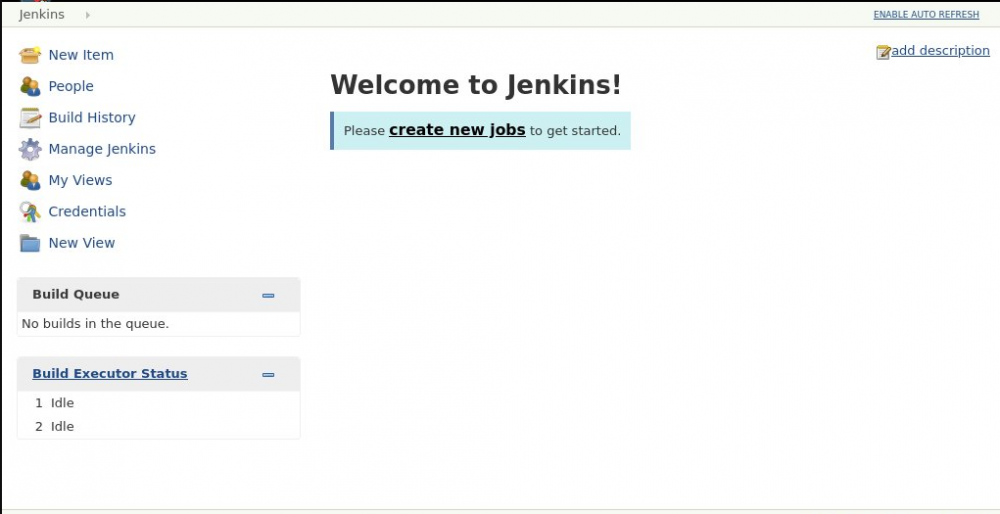
Now, Jenkins has been successfully installed on your Ubuntu 18.04 system.
Conclusion
You have successfully installed and configured Jenkins on your Ubuntu 18.04 server.
Check out these top 3 Linux hosting services
0