In most cases the means we use to delete a file from our computers such as using Delete key, Trash files or rm command, which do not permanently and securely remove the file from the hard disk (or any storage media).
The file is simply hidden from users and it resides somewhere on the hard disk. It can be recovered by data thieves, law enforcement or other threats.
Suggested Read: 3 Ways to Delete All Files in a Directory Except One or Few Files
Assuming a file contains classified or secret content such as usernames and passwords of a security system, an attacker with the necessary knowledge and skills can easily recover a deleted copy of the file and access these user credentials (and you can probably guess the aftermath of such as scenario).
In this article, we will explain a number of command line tools for permanently and securely deleting files in Linux.
1. Shred – Overwrite a File to Hide Content
shred overwrites a file to hide its contents, and can optionally delete it as well.
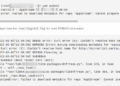
$ shred -zvu -n 5 passwords.list
In the command below, the options:
-z– adds a final overwrite with zeros to hide shredding-v– enables display of operation progress-u– truncates and removes file after overwriting-n– specifies number of times to overwrite file content (the default is 3)

shred – overwrite a file to hide its contents
You can find more usage options and information in the shred man page:
$ man shred
2. Wipe – Securely Erase Files in Linux
A Linux wipe command securely erases files from magnetic memory and thereby making it impossible to recover deleted files or directory content.
First, you need to install wipe tool in order to it, run the appropriate command below:
$ sudo apt-get install wipe [On Debian and its derivatives] $ sudo yum install wipe [On RedHat based systems]
The following command will destroy everything under the directory private.
$ wipe -rfi private/*
where the flags used:
-r– tells wipe to recurse into subdirectories-f– enables forced deletion and disable confirmation query-i– shows progress of deletion process

Wipe – Securely Erase Files in Linux
Note: Wipe only works reliably on magnetic memory, therefore use the other methods for solid state disks (memory).
Read through the wipe man page for additional usage options and instructions:
$ man wipe
3. Secure-deletetion Toolkit for Linux
Secure-delete is a collection of secure file deletion tools, that contains srm (secure_deletion) tool, which is used to remove files securely.
First you need to install it using the relevant command below:
$ sudo apt-get install secure-delete [On Debian and its derivatives] $ sudo yum install secure-delete [On RedHat based systems]
Once installed, you can use srm tool to remove files or directories securely on a Linux system as follows.
$ srm -vz private/*
where the options used:
-v– enables verbose mode-z– wipes the last write with zeros instead of random data

srm – Securely Delete Files in Linux
Read through the srm man page for more usage options and information:
$ man srm
4. sfill -Secure Free Disk/Inode Space Wiper
sfill is a part of secure-deletetion toolkit, is a secure free disk and inode space wiper, it deletes files on free disk space in a secure method. sfill checks the the free space on the specified partition and fills it with random data from /dev/urandom.
The command below will execute sfill on my root partition, with the -v switch enabling verbose mode:
$ sudo sfill -v /home/aaronkilik/tmp/
Assuming you created a separate partition, /home to store normal system users home directories, you can specify a directory on that partition to apply sfill on it:
$ sudo sfill -v /home/username
The are a few limitations of sfill that you can read about in the man page, where you can also find additional usage flags and instructions:
$ man sfill
Note: These following two tools (sswap and sdmem) in the secure-deletetion toolkit are not directly relevant for the scope of this guide, however, we will explain them for knowledge purpose and future use.
5. sswap – Secure Swap Wiper
It is a secure partition wiper, sswap deletes data present on your swap partition in a secure manner.
Caution: remember to unmount your swap partition before using sswap! Otherwise your system might crash!
Simply determine you swap partition (and check if paging and swapping devices/files are turned on using swapon command), next, disable paging and swapping devices/files with swapoff command (renders swap partition unusable).
Then run sswap command on the swap partition:
$ cat /proc/swaps $ swapon $ sudo swapoff /dev/sda6 $ sudo sswap /dev/sda6 #this command may take some time to complete with 38 default passes

sswap – Secure Swap Wiper
Make an effort to read through the sswap man page for more usage options and information:
$ man sswap
6. sdmem – Secure Memory Wiper
sdmem is a secure memory wiper, it is designed to remove data present in your memory (RAM) in a secure manner.
It was originally named smem, but because on Debain systems there exists another package called smem – report memory consumption on per-process and per-user basis, the developer decided to rename it sdmem.
$ sudo sdmem -f -v
For more usage information, read through the sdmem man page:
$ man sdmem
Suggested Read: PhotoRec – Recover Deleted or Lost Files in Linux
That’s it! In this article, we reviewed a number command line tools for permanently as well as securely deleting files in Linux. As usual, offer your thoughts or suggestions about the post via the comment form below.
Source: tecmint.com