Adapting to using the command line or terminal can be very hard for beginners who want to learn Linux. Because the terminal gives more control over a Linux system than GUIs programs, one has to get a used to running commands on the terminal. Therefore to memorize different commands in Linux, you should use the terminal on a daily basis to understand how commands are used with different options and arguments.

Manage File Types and Set Time in Linux – Part 3
Please go through our previous parts of this Linux Tricks series.
- 5 Interesting Command Line Tips and Tricks in Linux – Part 1
- 10 Useful Commandline Tricks for Newbies – Part 2
In this article, we are going to look at some tips and tricks of using 10 commands to work with files and time on the terminal.
File Types in Linux
In Linux, everything is considered as a file, your devices, directories and regular files are all considered as files.
There are different types of files in a Linux system:
- Regular files which may include commands, documents, music files, movies, images, archives and so on.
- Device files: which are used by the system to access your hardware components.
There are two types of device files block files that represent storage devices such as harddisks, they read data in blocks and character files read data in a character by character manner.
- Hardlinks and softlinks: they are used to access files from any where on a Linux filesystem.
- Named pipes and sockets: allow different processes to communicate with each other.
1. Determining the type of a file using ‘file’ command
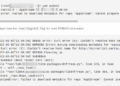
You can determine the type of a file by using the file command as follows. The screenshot below shows different examples of using the file command to determine the types of different files.
[email protected] ~/Linux-Tricks $ dir BACKUP master.zip crossroads-stable.tar.gz num.txt EDWARD-MAYA-2011-2012-NEW-REMIX.mp3 reggea.xspf Linux-Security-Optimization-Book.gif tmp-link [email protected] ~/Linux-Tricks $ file BACKUP/ BACKUP/: directory [email protected] ~/Linux-Tricks $ file master.zip master.zip: Zip archive data, at least v1.0 to extract [email protected] ~/Linux-Tricks $ file crossroads-stable.tar.gz crossroads-stable.tar.gz: gzip compressed data, from Unix, last modified: Tue Apr 5 15:15:20 2011 [email protected] ~/Linux-Tricks $ file Linux-Security-Optimization-Book.gif Linux-Security-Optimization-Book.gif: GIF image data, version 89a, 200 x 259 [email protected] ~/Linux-Tricks $ file EDWARD-MAYA-2011-2012-NEW-REMIX.mp3 EDWARD-MAYA-2011-2012-NEW-REMIX.mp3: Audio file with ID3 version 2.3.0, contains: MPEG ADTS, layer III, v1, 192 kbps, 44.1 kHz, JntStereo [email protected] ~/Linux-Tricks $ file /dev/sda1 /dev/sda1: block special [email protected] ~/Linux-Tricks $ file /dev/tty1 /dev/tty1: character special
2. Determining the file type using ‘ls’ and ‘dir’ commands
Another way of determining the type of a file is by performing a long listing using the ls and dir commands.
Using ls -l to determine the type of a file.
When you view the file permissions, the first character shows the file type and the other charcters show the file permissions.
[email protected] ~/Linux-Tricks $ ls -l total 6908 drwxr-xr-x 2 tecmint tecmint 4096 Sep 9 11:46 BACKUP -rw-r--r-- 1 tecmint tecmint 1075620 Sep 9 11:47 crossroads-stable.tar.gz -rwxr----- 1 tecmint tecmint 5916085 Sep 9 11:49 EDWARD-MAYA-2011-2012-NEW-REMIX.mp3 -rw-r--r-- 1 tecmint tecmint 42122 Sep 9 11:49 Linux-Security-Optimization-Book.gif -rw-r--r-- 1 tecmint tecmint 17627 Sep 9 11:46 master.zip -rw-r--r-- 1 tecmint tecmint 5 Sep 9 11:48 num.txt -rw-r--r-- 1 tecmint tecmint 0 Sep 9 11:46 reggea.xspf -rw-r--r-- 1 tecmint tecmint 5 Sep 9 11:47 tmp-link
Using ls -l to determine block and character files.
[email protected] ~/Linux-Tricks $ ls -l /dev/sda1 brw-rw---- 1 root disk 8, 1 Sep 9 10:53 /dev/sda1 [email protected] ~/Linux-Tricks $ ls -l /dev/tty1 crw-rw---- 1 root tty 4, 1 Sep 9 10:54 /dev/tty1
Using dir -l to determine the type of a file.
[email protected] ~/Linux-Tricks $ dir -l total 6908 drwxr-xr-x 2 tecmint tecmint 4096 Sep 9 11:46 BACKUP -rw-r--r-- 1 tecmint tecmint 1075620 Sep 9 11:47 crossroads-stable.tar.gz -rwxr----- 1 tecmint tecmint 5916085 Sep 9 11:49 EDWARD-MAYA-2011-2012-NEW-REMIX.mp3 -rw-r--r-- 1 tecmint tecmint 42122 Sep 9 11:49 Linux-Security-Optimization-Book.gif -rw-r--r-- 1 tecmint tecmint 17627 Sep 9 11:46 master.zip -rw-r--r-- 1 tecmint tecmint 5 Sep 9 11:48 num.txt -rw-r--r-- 1 tecmint tecmint 0 Sep 9 11:46 reggea.xspf -rw-r--r-- 1 tecmint tecmint 5 Sep 9 11:47 tmp-link
3. Counting number of files of a specific type
Next we shall look at tips on counting number of files of a specific type in a given directory using the ls, grep and wc commands. Communication between the commands is achieved through named piping.
- grep – command to search according to a given pattern or regular expression.
- wc – command to count lines, words and characters.
Counting number of regular files
In Linux, regular files are represented by the – symbol.
[email protected] ~/Linux-Tricks $ ls -l | grep ^- | wc -l 7
Counting number of directories
In Linux, directories are represented by the d symbol.
[email protected] ~/Linux-Tricks $ ls -l | grep ^d | wc -l 1
Counting number of symbolic and hard links
In Linux, symblic and hard links are represented by the l symbol.
[email protected] ~/Linux-Tricks $ ls -l | grep ^l | wc -l 0
Counting number of block and character files
In Linux, block and character files are represented by the b and c symbols respectively.
[email protected] ~/Linux-Tricks $ ls -l /dev | grep ^b | wc -l 37 [email protected] ~/Linux-Tricks $ ls -l /dev | grep ^c | wc -l 159
4. Finding files on a Linux system
Next we shall look at some commands one can use to find files on a Linux system, these include the locate, find, whatis and which commands.
Using the locate command to find files
In the output below, I am trying to locate the Samba server configuration for my system.
[email protected] ~/Linux-Tricks $ locate samba.conf /usr/lib/tmpfiles.d/samba.conf /var/lib/dpkg/info/samba.conffiles
Using the find command to find files
To learn how to use the find command in Linux, you can read our following article that shows more than 30+ practical examples and usage of find command in Linux.
- 35 Examples of ‘find’ Command in Linux
Using the whatis command to locate commands
The whatis command is mostly used to locate commands and it is special because it gives information about a command, it also finds configurations files and manual entries for a command.
[email protected] ~/Linux-Tricks $ whatis bash bash (1) - GNU Bourne-Again SHell [email protected] ~/Linux-Tricks $ whatis find find (1) - search for files in a directory hierarchy [email protected] ~/Linux-Tricks $ whatis ls ls (1) - list directory contents
Using which command to locate commands
The which command is used to locate commands on the filesystem.
[email protected] ~/Linux-Tricks $ which mkdir /bin/mkdir [email protected] ~/Linux-Tricks $ which bash /bin/bash [email protected] ~/Linux-Tricks $ which find /usr/bin/find [email protected] ~/Linux-Tricks $ $ which ls /bin/ls
5. Working with time on your Linux system
When working in a networked environment, it is a good practice to keep the correct time on your Linux system. There are certain services on Linux systems that require correct time to work efficiently on a network.
We shall look at commands you can use to manage time on your machine. In Linux, time is managed in two ways: system time and hardware time.
The system time is managed by a system clock and the hardware time is managed by a hardware clock.
To view your system time, date and timezone, use the date command as follows.
[email protected] ~/Linux-Tricks $ date Wed Sep 9 12:25:40 IST 2015
Set your system time using date -s or date –set=”STRING” as follows.
[email protected] ~/Linux-Tricks $ sudo date -s "12:27:00" Wed Sep 9 12:27:00 IST 2015 [email protected] ~/Linux-Tricks $ sudo date --set="12:27:00" Wed Sep 9 12:27:00 IST 2015
You can also set time and date as follows.
[email protected] ~/Linux-Tricks $ sudo date 090912302015 Wed Sep 9 12:30:00 IST 2015
Viewing current date from a calendar using cal command.
[email protected] ~/Linux-Tricks $ cal
September 2015
Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa
1 2 3 4 5
6 7 8 9 10 11 12
13 14 15 16 17 18 19
20 21 22 23 24 25 26
27 28 29 30
View hardware clock time using the hwclock command.
[email protected] ~/Linux-Tricks $ sudo hwclock Wednesday 09 September 2015 06:02:58 PM IST -0.200081 seconds
To set the hardware clock time, use hwclock –set –date=”STRING” as follows.
[email protected] ~/Linux-Tricks $ sudo hwclock --set --date="09/09/2015 12:33:00" [email protected] ~/Linux-Tricks $ sudo hwclock Wednesday 09 September 2015 12:33:11 PM IST -0.891163 seconds
The system time is set by the hardware clock during booting and when the system is shutting down, the hardware time is reset to the system time.
Therefore when you view system time and hardware time, they are the same unless when you change the system time. Your hardware time may be incorrect when the CMOS battery is weak.
You can also set your system time using time from the hardware clock as follows.
$ sudo hwclock --hctosys
It is also possible to set hardware clock time using the system clock time as follows.
$ sudo hwclock --systohc
To view how long your Linux system has been running, use the uptime command.
[email protected] ~/Linux-Tricks $ uptime 12:36:27 up 1:43, 2 users, load average: 1.39, 1.34, 1.45 [email protected] ~/Linux-Tricks $ uptime -p up 1 hour, 43 minutes [email protected] ~/Linux-Tricks $ uptime -s 2015-09-09 10:52:47
Summary
Understanding file types is Linux is a good practice for begginers, and also managing time is critical especially on servers to manage services reliably and efficiently. Hope you find this guide helpful. If you have any additional information, do not forget to post a comment. Stay connected to Tecmint.
Source: tecmint.com