Icinga 2 is a popular open source network resource monitoring system, and Icinga Web 2 is a web interface for Icinga 2. This article will describe how to install them on a CentOS 7 server.
Prerequisites
- A fresh Vultr CentOS 7 server instance.
- A sudo user.
Step 1: Update the system
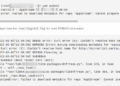
sudo yum install epel-release -y
sudo yum update -y
sudo shutdown -r now
After the reboot, use the same sudo user to log in.
Step 2: Install Apache
Install Apache using YUM:
sudo yum install httpd -y
Disable the pre-set Apache welcome page:
sudo sed -i 's/^/#&/g' /etc/httpd/conf.d/welcome.conf
Forbid Apache from exposing files and directories within the web root directory /var/www/html to visitors:
sudo sed -i "s/Options Indexes FollowSymLinks/Options FollowSymLinks/" /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
Start the Apache service and get it started on boot:
sudo systemctl start httpd.service
sudo systemctl enable httpd.service
Step 3: Install MariaDB
Install MariaDB using YUM:
sudo yum install mariadb mariadb-server -y
Start the MariaDB service:
sudo systemctl start mariadb.service
sudo systemctl enable mariadb.service
Secure the installation of MariaDB:
sudo /usr/bin/mysql_secure_installation
During the process, answer questions on the screen as below:
Enter current password for root (enter for none): Enter
Set root password? [Y/n]: Y
New password: <your-password>
Re-enter new password: <your-password>
Remove anonymous users? [Y/n]: Y
Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n]: Y
Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n]: Y
Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n]: Y
Step 4: Install PHP
Install PHP and necessary PHP extensions as required by Icinga 2 and Icinga Web 2:
sudo yum install php php-gd php-intl php-ldap php-ZendFramework php-ZendFramework-Db-Adapter-Pdo-Mysql -y
Then you need to setup the proper timezone for your machine, which can be determined from the PHP official website. On my server instance, the timezone value is “America/Los_Angeles”.
Open the PHP configuration file with the vi editor:
sudo vi /etc/php.ini
Find the line:
;date.timezone =
Change it to:
date.timezone = America/Los_Angeles
Save and quit:
:wq!
Restart the Apache service in order to put new configurations into effect:
sudo systemctl restart httpd.service
Step 5: Install Icinga 2 and its plugins
On CentOS 7, you can install Icinga 2 and its plugins using the icinga YUM repo:
sudo rpm --import http://packages.icinga.org/icinga.key
sudo rpm -i https://packages.icinga.org/epel/7/release/noarch/icinga-rpm-release-7-1.el7.centos.noarch.rpm
sudo yum install icinga2 nagios-plugins-all -y
You can learn more about these plugins from the Monitoring Plugins Project.
Start the Icinga 2 service:
sudo systemctl start icinga2.service
sudo systemctl enable icinga2.service
By default, the Icinga 2 program will enable three features: checker, mainlog, and notification. You can verify that using the following command:
sudo icinga2 feature list
Step 6: Setup the Icinga 2 IDO modules
6.1) Install the IDO (Icinga Data Output) modules for MySQL
sudo yum install icinga2-ido-mysql -y
6.2) Create a database for Icinga 2
Log into the MySQL shell as root:
mysql -u root -p
Use the MariaDB root password you set in step 3 to log in.
Create a database named “icinga” and a database user named icinga with the password icinga, and then grant privileges on this database to this database user.
CREATE DATABASE icinga;
GRANT SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, DROP, CREATE VIEW, INDEX, EXECUTE ON icinga.* TO 'icinga'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'icinga';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
EXIT;
6.3) Import the Icinga 2 IDO schema
mysql -u root -p icinga < /usr/share/icinga2-ido-mysql/schema/mysql.sql
When prompted, input the MariaDB root password to finish the job.
6.4) Enable the IDO MySQL module
sudo vi /etc/icinga2/features-available/ido-mysql.conf
Find these lines:
//user = "icinga"
//password = "icinga"
//host = "localhost"
//database = "icinga"
uncomment them as below:
user = "icinga"
password = "icinga"
host = "localhost"
database = "icinga"
Save and quit:
:wq!
Enable the ido-mysql feature:
sudo icinga2 feature enable ido-mysql
sudo systemctl restart icinga2.service
Step 7: Install Icinga Web 2
7.1) Setup external command pipe
sudo icinga2 feature enable command
sudo systemctl restart icinga2.service
Before you can send commands to Icinga 2 using a web interface, you need to add the “apache” user to the icingacmd group:
sudo usermod -a -G icingacmd apache
You can verify your modification using the following command:
id apache
7.2) Install the icingaweb2 and icingacli RPM packages
sudo yum install icingaweb2 icingacli -y
Point the Apache web root directory to the location of Icinga Web 2:
sudo icingacli setup config webserver apache --document-root /usr/share/icingaweb2/public
sudo systemctl restart httpd.service
7.3) Generate a setup token for later use in the web interface
sudo icingacli setup token create
7.4) Modify firewall rules in order to allow web access
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --add-service=http
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
7.5) Initiate the Icinga 2 installation wizard in the web interface
Point your web browser to the following URL:
http://<your-server-ip>/icingaweb2/setup
7.6) On the Welcome page, input the setup token you generated earlier, and then click the “Next” button.
7.7) On the Modules page, select modules you want to enable (at least, the Monitoring module is required), and then click the “Next” button.
7.8) On the Requirements page, make sure that every requirement item is satisfied, and then click the “Next” button.
7.9) On the Authentication page, you need to choose the authentication method when accessing Icinga Web 2. Here, you can choose Database, and then click the “Next” button.
7.10) On the Database Resource page, fill out all required fields as below, and then click the “Next” button.
- Resource Name*: icingaweb_db
- Database Type*: MySQL
- Host*: localhost
- Database Name*: icingaweb2
- Username*: root
- Password*:
<MariaDB-root-password>
7.11) On the Authentication Backend page, using the default backend name icingaweb2, click the Next button to move on.
7.12) On the Administration page, setup the first Icinga Web 2 administrative account (say it is icingaweb2admin) and password (icingaweb2pass), and then click the “Next” button.
7.13) On the Application Configuration page, you can adjust application- and logging-related configuration options to fit your needs. For now, you can use the default values listed below and click the “Next” button to proceed.
- Show Stacktraces: Checked
- User Preference Storage Type*: Database
- Logging Type*: Syslog
- Logging Level*: Error
- Application Prefix*: icingaweb2
7.14) On the Review page, double check your configuration, and then click the Next button.
7.15) On the Monitoring Module Configuration Welcome page, click the Next button.
7.16) On the Monitoring Backend page, use the default backend name icinga and backend type IDO, and then click the “Next” button.
7.17) On the Monitoring IDO Resource page, input IDO database details you setup earlier, and then click the “Next” button.
- Resource Name*: icinga_ido
- Database Type*: MySQL
- Host*: localhost
- Database Name*: icinga
- Username*: icinga
- Password*: icinga
7.18) On the Command Transport page, still use these default values listed below. Click the Next button to move on.
- Transport Name*: icinga2
- Transport Type*: Local Command File
- Command File*:
/var/run/icinga2/cmd/icinga2.cmd
7.19) On the Monitoring Security page, still use the default value:
- Protected Custom Variables: *pw*,*pass*,community
Click the “Next” button to go to next page.
7.20) On the review page, double check your configuration, and then click the Finish button.
7.21) On the Congratulations! page, click the Login to Icinga Web 2 button to jump to the Icinga Web 2 login page. Use the Icinga Web 2 administrative account and password you setup earlier to log in. Feel free to explore the Icinga Web 2 dashboard.
That concludes our tutorial. Thank you for reading.
Want to contribute?
You could earn up to $300 by adding new articles
Suggest an update
Request an article