Download a Local Copy of your Linode Backup
The Linode Backups service can create automatic and manual snapshots of your Linode. A completed backup can be directly restored to the origin Linode or to a new Linode in the same data center. These workflows make it easy to revert to a working configuration if you run into any unexpected issues with your software.
Linode’s backups are stored in a way that is only directly readable by the Linode Backups service. A common question for the service is how you can download the content from your Linode Backups to another storage location, like your home computer. This can be accomplished in two phases:
- Restore a backup to a new Linode in the same data center.
- Download either specific files or the entire disk image from that Linode, as needed.
Before You Begin
Account Permissions and Billing
Several of the steps in this guide involve adding services to or removing services from a Linode account. Visit our guide on Users and Permissions for more information about restricted Linode users.
Note that the cost of adding Backups service and adding a Linode to your account is billed, prorated per hour. If the backups service is only enabled for a few hours, you will only be charged for a few hours of the service. See the Backups pricing details for more information. Likewise, when you create a Linode, you will be billed per hour that the Linode exists, whether it is powered on or not.
The steps in this guide have been designed to minimize the potential costs associated with this process. Additionally, keep the following in mind:
- Removing a Linode from your account also cancels the associated Backup service for that Linode.
- A Linode’s backups are deleted when a Linode is deleted.
- If you choose to leave the Backups service enabled, or if you do not remove the additional Linode from your account, you will be automatically billed. If you only power the Linode off, you will still be billed for it.
Enable Backups and Take a Snapshot
These steps are the minimum required for the scope of this guide. Visit our Backups guide for information about how to implement regular backups of your Linode.
-
Go to your Linode’s dashboard, click Backups, click Enable backups for this Linode » and confirm the additional cost per month.
-
This guide focuses on saving a snapshot or specific backup. Click Take a New Snapshot Now.
- The snapshot appears in the Backup History at the bottom of the page.
Restore from a Backup
This section shows how to restore a backup to a new Linode, or to an existing Linode.
Restoring a backup will create a new configuration profile and a new set of disks on your Linode. The restore process does not restore single files or directories automatically. Restoring particular files can be done by completing a normal restore, copying the files off of the new disks, and then removing the disks afterward.
Note
The size of the disk(s) created by the restore process will only be slightly larger than the total size of the files restored. This means that the disk(s) created will be ‘full’.
Some applications, like databases, need some amount of free unused space inside the disk in order to run. As a result, you may want to increase your disk(s) size after the restore process is completed.
To restore a backup to a different data center, first restore to a Linode in the same data center, creating a new one if necessary. Once the restore is complete, use the Clone tab to copy the disk(s) to a Linode in a different data center.
Restore to a New Linode
You can restore a backup to any Linode located in the same data center, even if the target does not have the Backup Service enabled. This section covers how to restore a backup to a new Linode that does not have any disks deployed to it. If you wish to restore your backup to an existing Linode, see the next section.
-
From the Dashboard of the Linode whose backups you intend to restore, click on the Backups tab. Select the Restore to… link beneath the backup version that you want to restore.
-
Under the Select column, click the Restore to this Linode link next to your new Linode:
The backup disks and configuration profiles will be restored to the Linode you selected. Watch the Host Job Queue to monitor the progress. Restoring from a backup can take several minutes depending on the size of your Linode and the amount of data you have stored on it.
Restore to an Existing Linode
To restore a backup to an existing Linode, you will need to make sure that you have enough storage space that is not currently assigned to disk images.
Note
If you are attempting to restore a disk to the same Linode the backup was created from, the restoration process will not delete the original disk for you. Manually delete the original disk to make room for the backup.
-
Start by confirming the size of the backup that you wish to restore. From the Backups tab in your Linode’s Dashboard, click the Restore to… link beneath your desired backup version.
-
Check the Total size required field to confirm the size of your backup.
As an example, if the total size of the backup comes to 3107MB, this means you would need at least that much free space to restore the backup to your Linode.
-
Next, you’ll confirm the total space assigned to disk images on your Linode, via the Storage indicator on your Linode’s Dashboard.
-
If the amount of space available is greater than the size of the backup, you can proceed with restoring. If the amount of unallocated space is less than the size of the backup, you can resize your existing disks to make room for it.
Note
In some cases, you will not be able to shrink your disks enough to fit the restored backup. As an alternative, you can change your Linode’s plan to a higher tier that offers more disk space. -
Once the disk resize has completed, check the storage indicator on your Linode’s Dashboard to confirm that you’ve freed up enough space for your backup.
-
From the Backups tab, click the Restore to this Linode link next to your Linode.
Your backup will begin restoring to your Linode, and you can monitor its progress from the Host Job Queue in your Linode’s Dashboard tab. Note that the time it takes to restore your backup will vary depending upon the restore size, and the number of files being restored.
Download Specific Files or Directories over SSH
If you just need specific files from your Linode, you can download those over SSH. In order to do so, you’ll first need to reboot your Linode under the new configuration profile that was created by the restore process. This new profile is assigned to the restored disks, and your backed up data will be accessible when you boot from them.
Downloading files over SSH can be done at a command-line interface, or with a graphical SFTP file browser.
Using SCP
To retrieve a specific directory or file via the command-line, you can use the secure copy (SCP) command from your computer. SCP is installed by default on most Mac and Linux systems, and you can install a tool like Cygwin to use it on Windows.
-
The syntax for using SCP to copy a file from your Linode into a directory on your computer is:
scp your_linode_username@your_linode_ip:/path/to/your/file.txt /path/to/your/local/directory/The file will be saved inside
/path/to/your/local/directory/on your computer. -
To copy a file from your Linode to your computer and give it a specific name (in this case,
file.txt.backup):scp your_linode_username@your_linode_ip:/path/to/your/file.txt /path/to/your/local/directory/file.txt.backup -
To copy a directory from your Linode to your computer:
scp -r your_linode_username@your_linode_ip:/path/to/your/directory /path/to/your/local/directoryIf
/path/to/your/local/directoryalready exists on your computer, then the copied directory will be placed inside/path/to/your/local/directory(i.e./path/to/your/local/directory/directory).If
/path/to/your/local/directorydoes not already exist, then the copied directory will be created with that name.
For example:
-
Download an NGINX configuration file to your home folder:
scp your_linode_username@your_linode_ip:/etc/nginx/conf.d/example.com.conf ~/example.com.conf.backup -
Download an Apache configuration file to your home folder:
scp your_linode_username@your_linode_ip:/etc/apache2/sites-available/example.com.conf ~/example.com.conf.backup -
Copy the entire document root from a web server:
scp -r your_linode_username@your_linode_ip:/var/www/html/ ~/html_backup
If you intend to repeat this process regularly, consider using rsync to create additional local copies of your data. rsync is capable of performing incremental file copies, which means you do not have to fully transfer each file every time you download your data.
Using FileZilla
As an alternative to the command-line, you can download and install an SFTP client. These applications provide a graphical user interface for your Linode’s filesystem.
FileZilla is a popular free example. Windows and OS X users can download FileZilla here. To install FileZilla on Linux:
-
Debian/Ubuntu:
sudo apt-get install filezilla -
CentOS/Fedora:
sudo yum install filezilla
After you’ve installed FileZilla on your computer:
-
Open FileZilla from your Windows start menu, OS X Launchpad, or the launcher provided by your Linux distribution of choice.
-
Enter your Linode’s IP address or domain name in the
Hostfield. Enter the account username you wish to connect as in theUsernamefield. Please note that this must be a user account on your Linode; if in doubt, enterrootto log in as the root user. Enter the account’s password in thePasswordfield, and enter “22” in thePortfield. Click Quickconnect to initiate the file transfer session.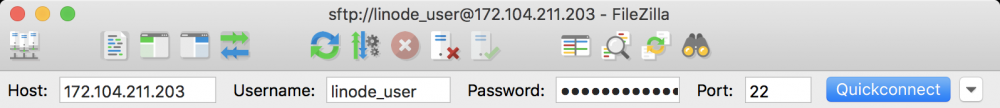
-
If this is the first time you’ve connected to your Linode with an SSH or SFTP program, you’ll receive a warning that the host key is unknown. Place a check mark in the box next to
Always trust this host, add this key to the cache. Checking this box prevents further warnings unless the key presented to FileZilla changes; this should only happen if you reinstall the remote server’s operating system.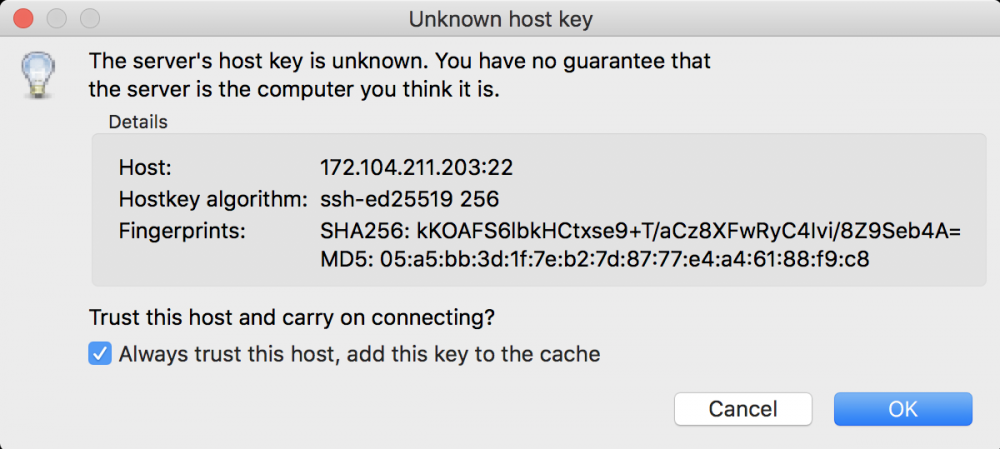
-
Click the OK button to proceed. You’ll be presented with a split view, with your local filesystem on the left and your Linode’s filesystem on the right. You may transfer files by dragging and dropping them between each side.
For more information on FileZilla, review our full guide on using the application.
Using mysqldump to Back Up a Database
Special care is needed when downloading data from a database. Before it can be downloaded, the data in a database needs to first be dumped to a file. This file can then be transferred just as any other normal file type.
The mysqldump command’s general syntax is:
mysqldump -u [username] -p [databaseName] > [filename]-$(date +%F).sql
mysqldumpprompts for a password before it starts the backup process.- Depending on the size of the database, it could take a while to complete.
- The database backup will be created in the directory the command is run.
-$(date +%F)adds a timestamp to the filename.
Example use cases include:
-
Create a backup of an entire Database Management System (DBMS):
mysqldump --all-databases --single-transaction --quick --lock-tables=false > full-backup-$(date +%F).sql -u root -p -
Back up a specific database. Replace
db1with the name of the database you want to back up:mysqldump -u username -p db1 --single-transaction --quick --lock-tables=false > db1-backup-$(date +%F).sql -
Back up a single table from any database. In the example below,
table1is exported from the databasedb1:mysqldump -u username -p --single-transaction --quick --lock-tables=false db1 table1 > db1-table1-$(date +%F).sql
Here’s a breakdown of the mysqldump command options used above:
--single-transaction: Issue a BEGIN SQL statement before dumping data from the server.--quick: Enforce dumping tables row by row. This provides added safety for systems with little RAM and/or large databases where storing tables in memory could become problematic.--lock-tables=false: Do not lock tables for the backup session.
For more information on MySQL database backups, including how to restore the data in a dump file to a MySQL installation, review our guide on the subject. An alternative to using mysqldump is to create physical backups. It’s also possible to backup PostgreSQL databases.
Download a Disk over SSH
Downloading your disk will copy a .img file to your computer that encapsulates all of the data that is on your Linode’s disk.
Prepare the Receiving Computer
Verify that the receiving computer has SSH installed. (Most Linux/Unix-like systems have it installed by default.) If you’re running Windows locally, you may wish to set up the Cygwin compatibility layer to provide a reasonably complete Unix-like environment. Instructions on setting up Cygwin are located here.
Start Your Linode in Rescue Mode
Before you initiate the transfer, start the source Linode in Rescue Mode and start SSH by following these guides:
- Start your Linode in Rescue Mode.
- Connecting to a Linode Running in Rescue Mode via LISH.
- Start the SSH server on your Linode.
Copy the Disk
Now that the Linode is running in Rescue Mode, you can transfer the disk from the Linode to the receiving machine over SSH:
-
Enter the following command on the receiving machine. Replace
123.45.67.89with the Linode’s IP address and/home/archive/linode.imgwith the path where you want to store the disk:ssh root@123.45.67.89 "dd if=/dev/sda " | dd of=/home/archive/linode.imgNote
The device/dev/sdais used for Linodes running on top of KVM. If your Linode is still using XEN, then throughout this guide you must use/dev/xvdainstead. -
The receiving machine will connect to the Linode. Type
yesand press Enter to continue connecting:The authenticity of host '123.45.67.89 (123.45.67.89)' can't be established. RSA key fingerprint is 39:6b:eb:05:f1:28:95:f0:da:63:17:9e:6b:6b:11:4a. Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes -
Enter the root password for the Linode:
Warning: Permanently added '123.45.67.89' (RSA) to the list of known hosts. root@123.45.67.89's password:The transfer starts, and you’ll see output similar to the following:
4096000+0 records in 4096000+0 records out 2097152000 bytes (2.1 GB) copied, 371.632 seconds, 5.6 MB/s 4096000+0 records in 4096000+0 records out 2097152000 bytes (2.1 GB) copied, 364.002 s, 5.8 MB/sNote
Copying your disk can take a while. Please be patient. If you have a slow internet connection, add the-Coption to the SSH command; this enables gzip compression for data transfer. If you receive aWrite failed: Broken pipeerror, repeat this process.
Verify the Disk
Once the copy has completed, you can verify it by mounting the image on the receiving machine.
-
Log in to the receiving machine as
rootby entering the following command and entering therootuser’s password:su -
Make a directory on the receiving machine by entering the following command:
mkdir linode -
Mount the disk by entering the following command, replacing
linode.imgwith the name of the disk:mount -o loop linode.img linode -
View the directories stored on the disk by entering the following command:
ls linode/You should see the directories on the disks, similar to the ones shown below, indicating that everything has transferred:
bin dev home lost+found mnt proc sbin srv tmp var boot etc lib media opt root selinux sys usr
Clean Up after Your Download
After you’ve finished downloading your files or disks, you can optionally delete the restored disks. If you created a new Linode to perform the restore, consider deleting the Linode. As a reminder, billing for that Linode will continue automatically if you do not remove it. If you only power the Linode off, you will still be billed for it.
Join our Community
Find answers, ask questions, and help others.
This guide is published under a CC BY-ND 4.0 license.


